Connected Insulin Pen (CIP) Toolkit
Interpretation of Connected Insulin Pen (CIP) Data
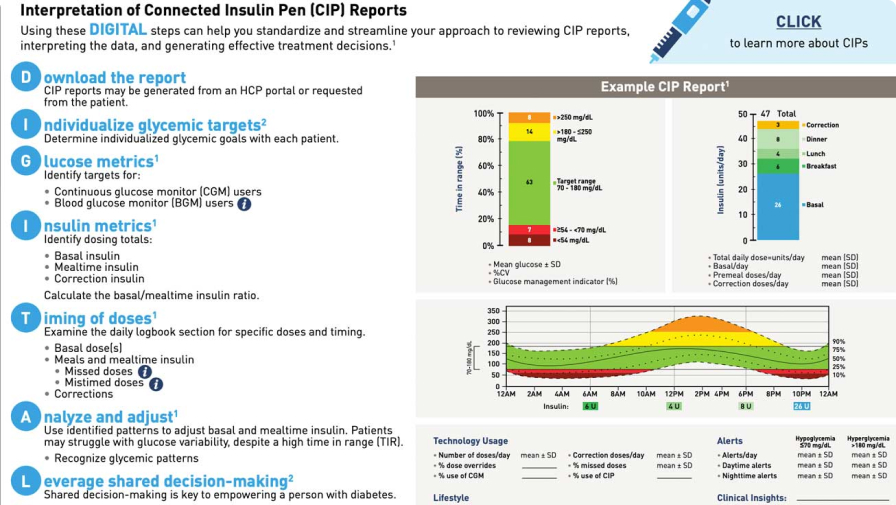
Using these DIGITAL steps can help you standardize and streamline your approach to reviewing CIP reports, interpreting the data, and generating effective treatment decisions.
D
I
G
- Continuous glucose monitor users
- Blood glucose monitor users
I
- Basal insulin
- Mealtime insulin
- Correction insulin
Calculate the basal/mealtime insulin ratio.
T
- Basal dose(s)
- Meals and mealtime insulin
- Missed doses
- Mistimed doses
- Corrections
A
- Recognize glycemic patterns
L
- Establish a collaborative relationship to support diabetes self-management
- A CIP not only connects insulin and glucose data, but also the healthcare professional and patient
Dr David Ahn walks through the Let’s Go DIGITAL steps for standardized CIP report interpretation.
Welcome! My name is David Ahn. I am a board-certified adult endocrinologist and program director at Mary & Dick Allen Diabetes Center for Hoag Memorial Hospital Presbyterian in Newport Beach, California. I love using technology to help empower patients and improve their ability to manage their diabetes.
One example is Connected Insulin Pens, or CIPs, which are becoming an important part of diabetes care and have become more common among patients with diabetes who are taking insulin injections. CIPs automatically record insulin dose information, removing the need for manual documentation.
In this video, I will show a standardized approach to reviewing CIP reports, so you can maximize their benefits for you and your patients. Each step in this approach follows the acronym DIGITAL, so let’s dive in and GO DIGITAL!
The first step is to download the report. Depending on the type of CIP, reports can be generated from an HCP portal or requested from the patient. This can be performed for an in-person visit, or reports may also be reviewed remotely.
Steps to make the process more efficient in your office could include uploading the PDF directly into your EHR, printing and scanning the report, or using your computer’s snipping tool to paste relevant images directly into your clinic note.
The next step is to individualize glycemic targets. Individualized glycemic goals should be determined with each patient. Recommendations, like those seen in this figure, can be used to guide individualized targets based on patient features. For example, older patients or those at risk for severe hypoglycemia might benefit from higher glycemic targets.
Sometimes, data downloads from diabetes devices can be overwhelming. So to break it down, I always focus first on glucose metrics.
For CGM users, the glucose management indicator, or GMI, can provide an estimated HbA1c for the period of the report.
Next review the time the patient spends in, above, and below target range. Additionally, assess glycemic variability by reviewing the coefficient of variation, or CV, and standard deviation of mean glucose. A percent CV of less than 36 is recommended by guidelines.
For your information, the CV is the percent calculation of the standard deviation divided by the mean blood sugar.
Also, don’t forget to note how much your patient is wearing their CGM. Patients should aim for more than 70% device wear time, which adds confidence that the data are an accurate reflection of the patient’s usual glycemic patterns.
For patients on intensive insulin therapies and using BGMs, encourage them to test frequently to ensure you have the data needed to make informed treatment decisions. This may include checking their blood glucose before eating, sleeping, physical activity, and performing critical tasks. As well as when they suspect their glucose levels may be outside of target range.
Next we move to insulin metrics. Identify the regimen and daily dose totals of basal, mealtime, and correction insulin for each patient.
Total daily insulin requirements can be estimated based on body weight, with typical doses ranging from 0.4 to 1.0 units/kg/day.
The ratio of basal to mealtime insulin can help assess situations of overbasalization, inadequate mealtime dosing, or overly aggressive mealtime doses.
Now with the integration of insulin and glucose data provided by a CIP, we can assess the timing of doses.
The day-to-day portion of the report can provide insight into the effect of mealtime doses on glucose.
Missed, mistimed, or inadequate doses may contribute to the frequency of hyper- and hypoglycemia. Understanding when, and if, your patient is taking their mealtime injections is KEY for making clinical recommendations for improvement.
We can use these data to analyze and adjust by evaluating glycemic patterns and fine-tuning basal and mealtime insulin dosing accordingly.
It is important to prioritize reducing hypoglycemia.
Also, consider comparing the current report to the one from the last visit to evaluate the impact of the previously implemented treatment plan.
Next, assess whether the patient is meeting their individual glucose targets. Even patients with a high time in range can struggle with glucose variability.
Identify any inadequate insulin dosing. Factor in other considerations such as inaccurate carb counting, fear of hypoglycemia, relative levels of physical activity, or a need for meal-to-meal dose adjustments.
Once you have a treatment plan in mind, it is time to leverage shared-decision making. Shared decision-making is key to empowering a person with diabetes and establishing a collaborative relationship that helps support diabetes self-management.
It is also important to remember that person-centered glycemic management is a cyclical process. Treatment decisions should be regularly reassessed by clinicians with people with diabetes.
Following these steps, a connected insulin pen has the potential to connect not only insulin and glucose data, but also health care providers with people with diabetes
That concludes our walkthrough of a standard CIP report. We hope the steps presented here will help you standardize and streamline your approach to reviewing CIP reports across platforms. You can find all of this information and more in the Let’s Go DIGITAL tip sheet in the Connected Insulin Pen Tool Kit on education.lillymedical.com.
Thank you for watching!
References
- ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al. Standards of care in diabetes–2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(suppl 1):S1-S291.
- Rodbard D, Garg SK. Standardizing reporting of glucose and insulin data for patients on multiple daily injections using connected insulin pens and continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(3):221-226.
VV-MED-154647
Please rate your satisfaction with the content on the following statements:
Very Dissatisfied
Dissatisfied
Neutral
Satisfied
Very Satisfied