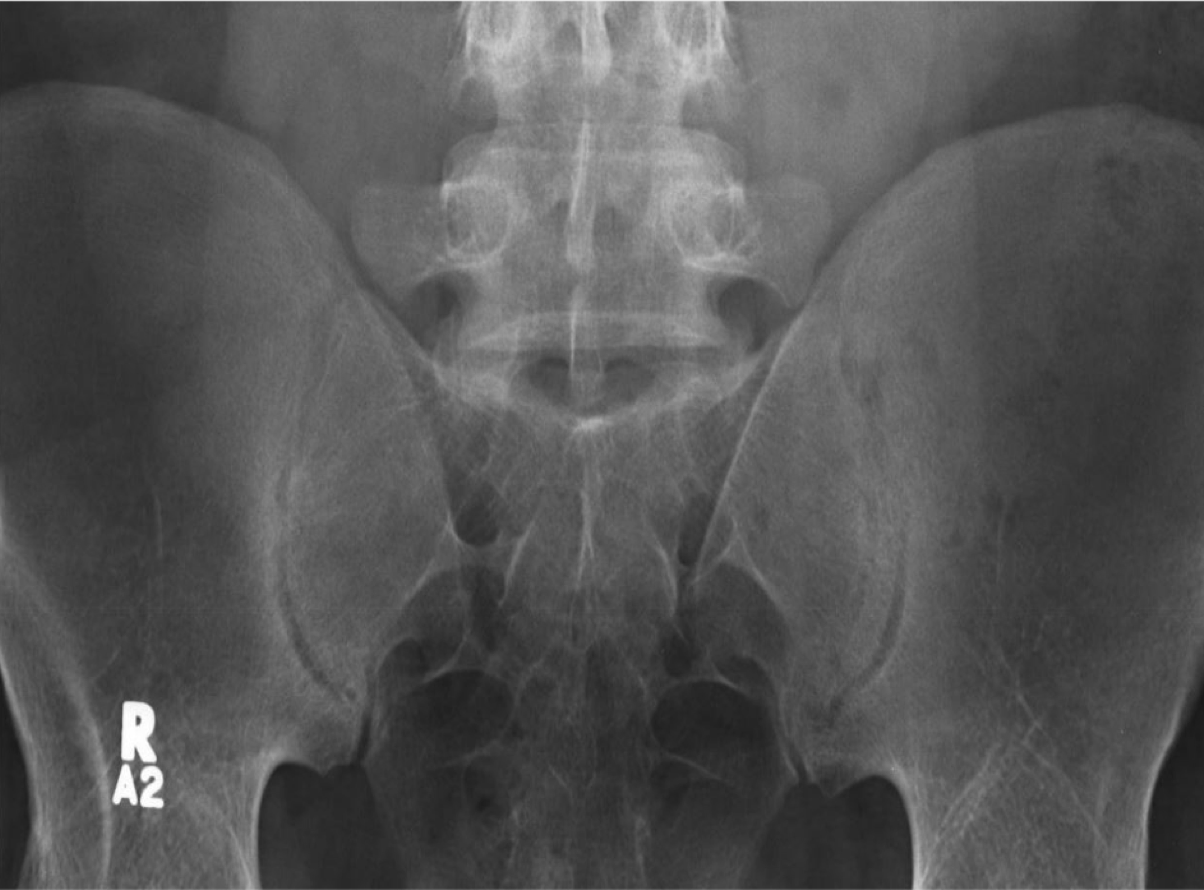
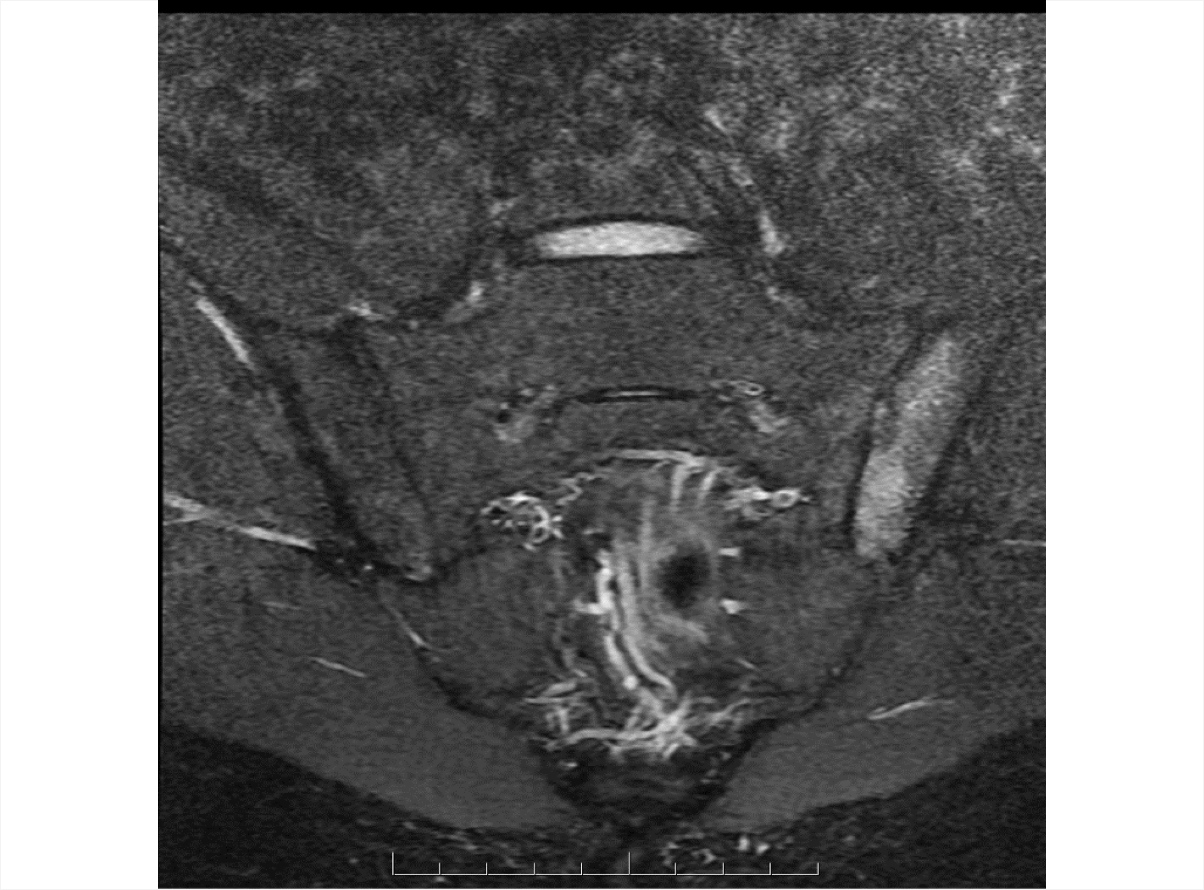
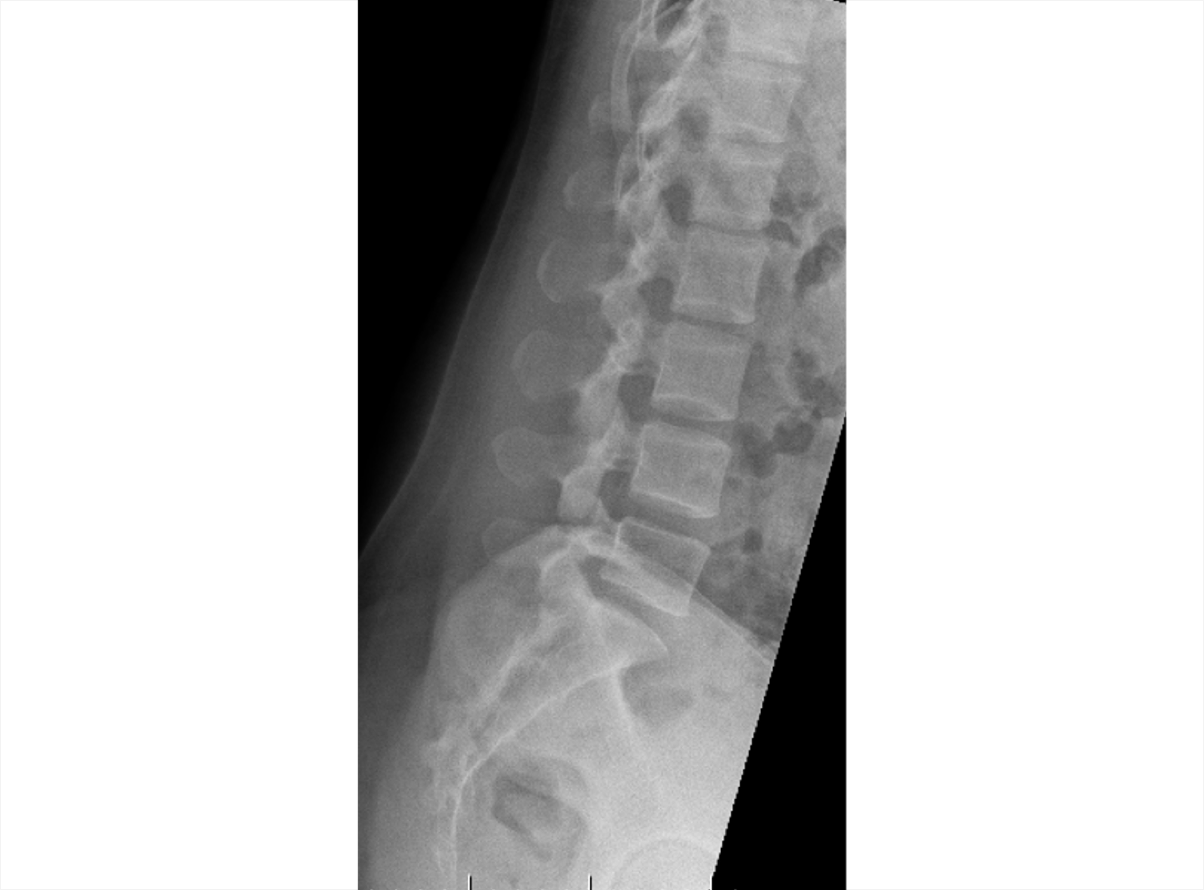
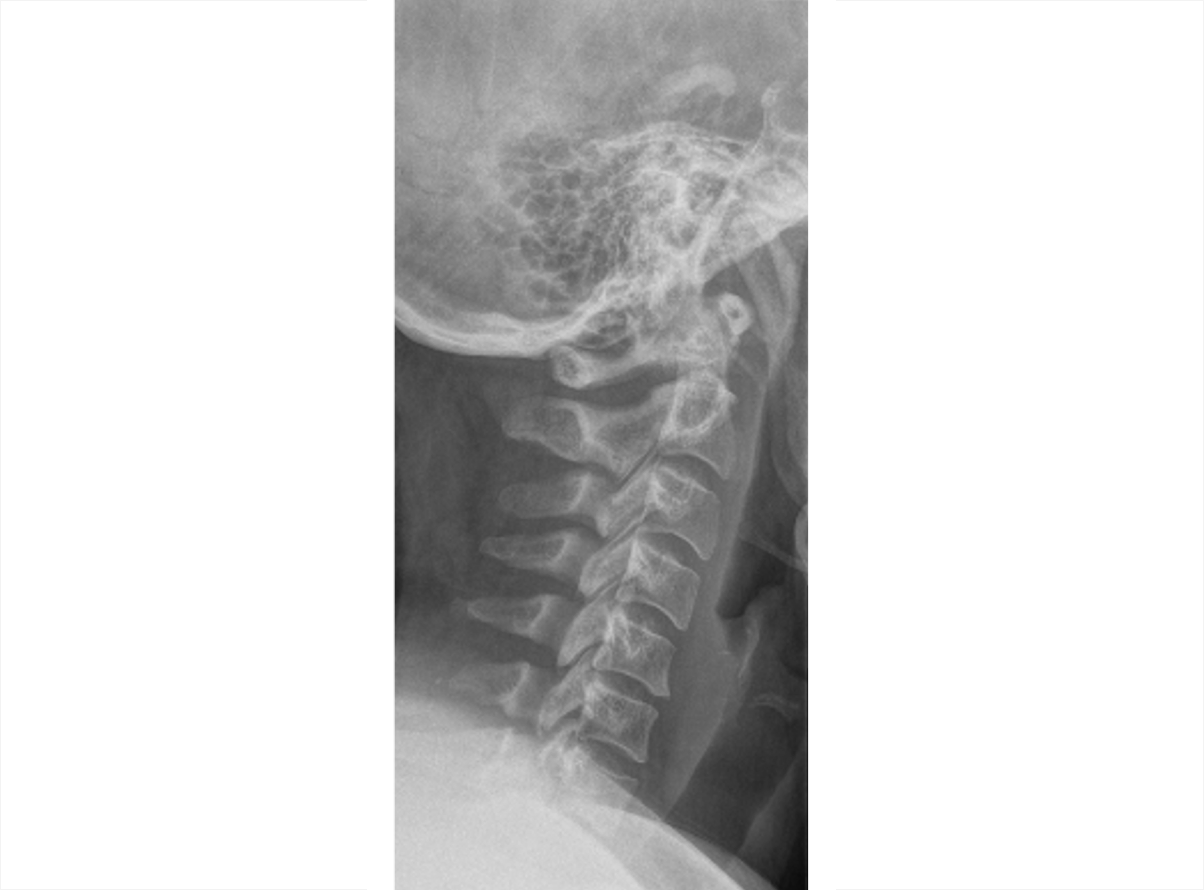
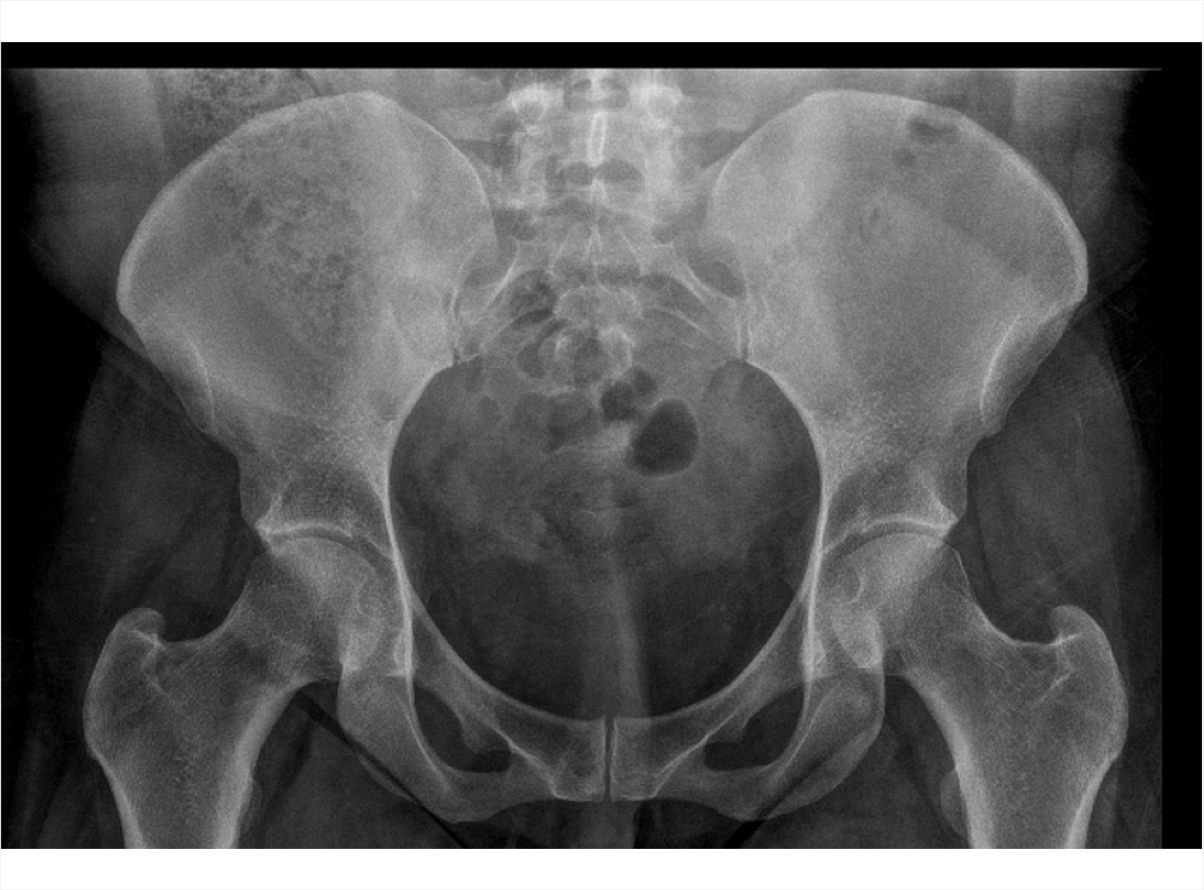
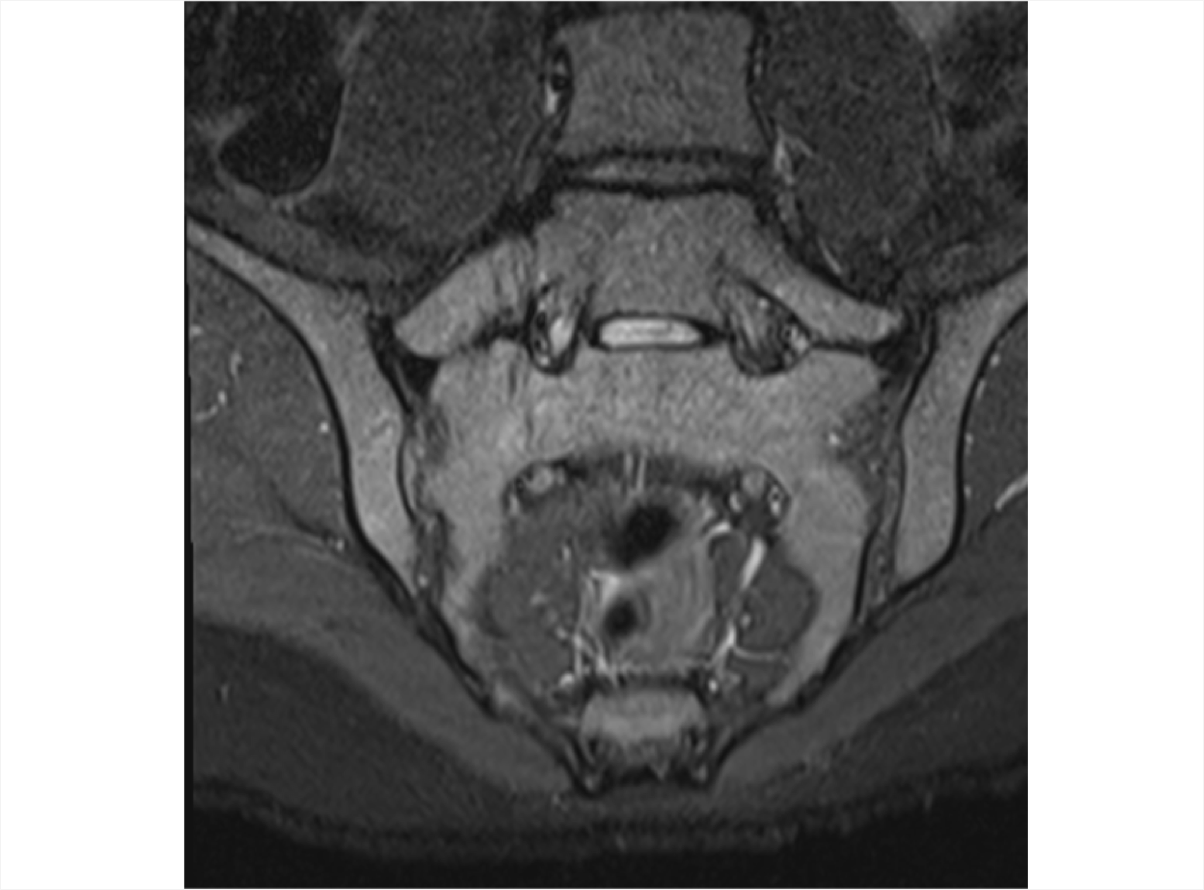
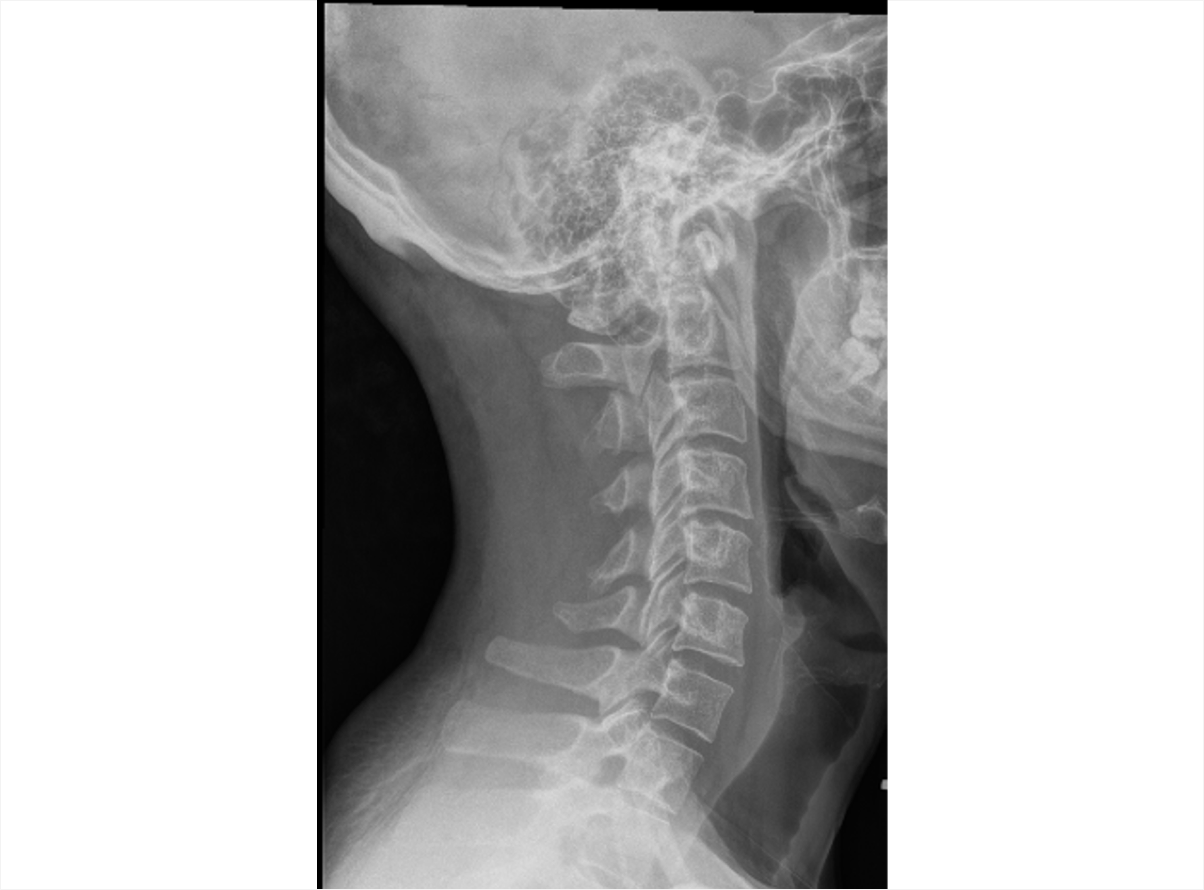
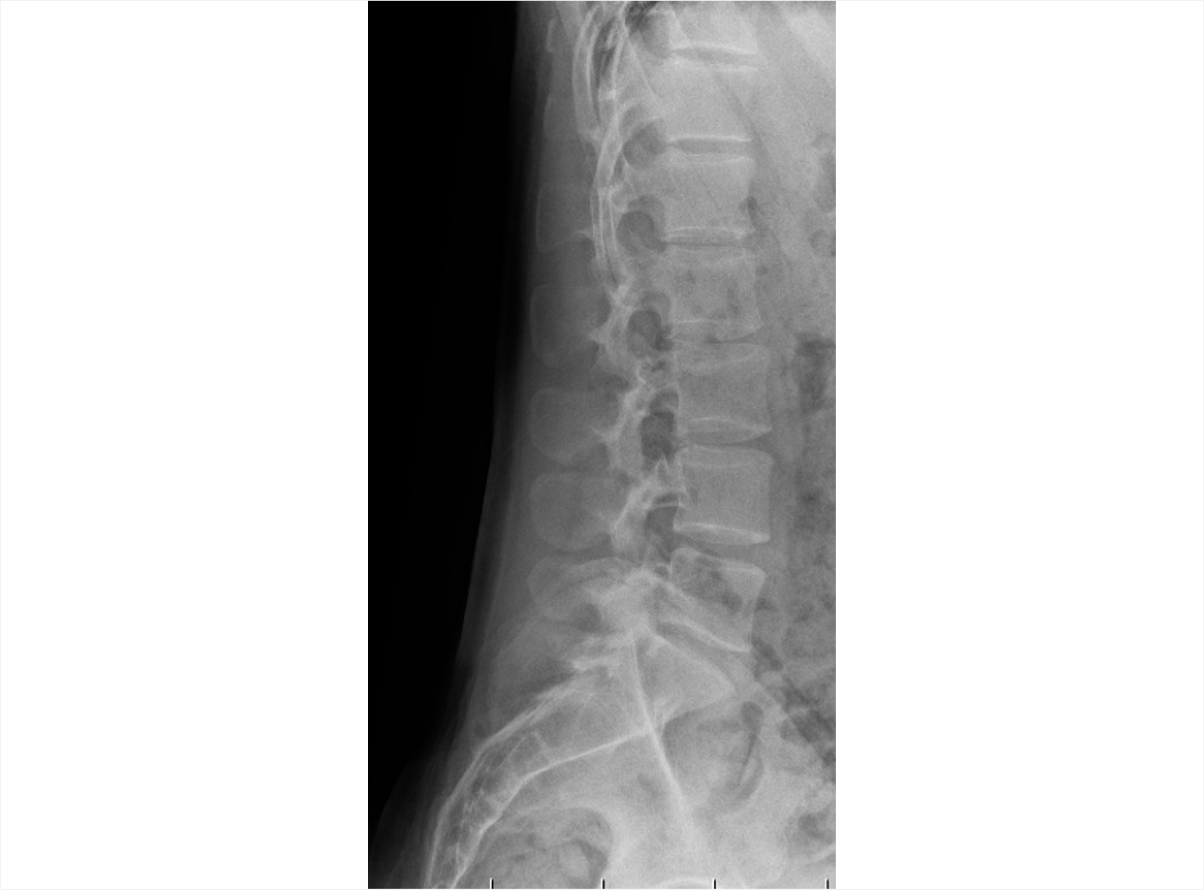
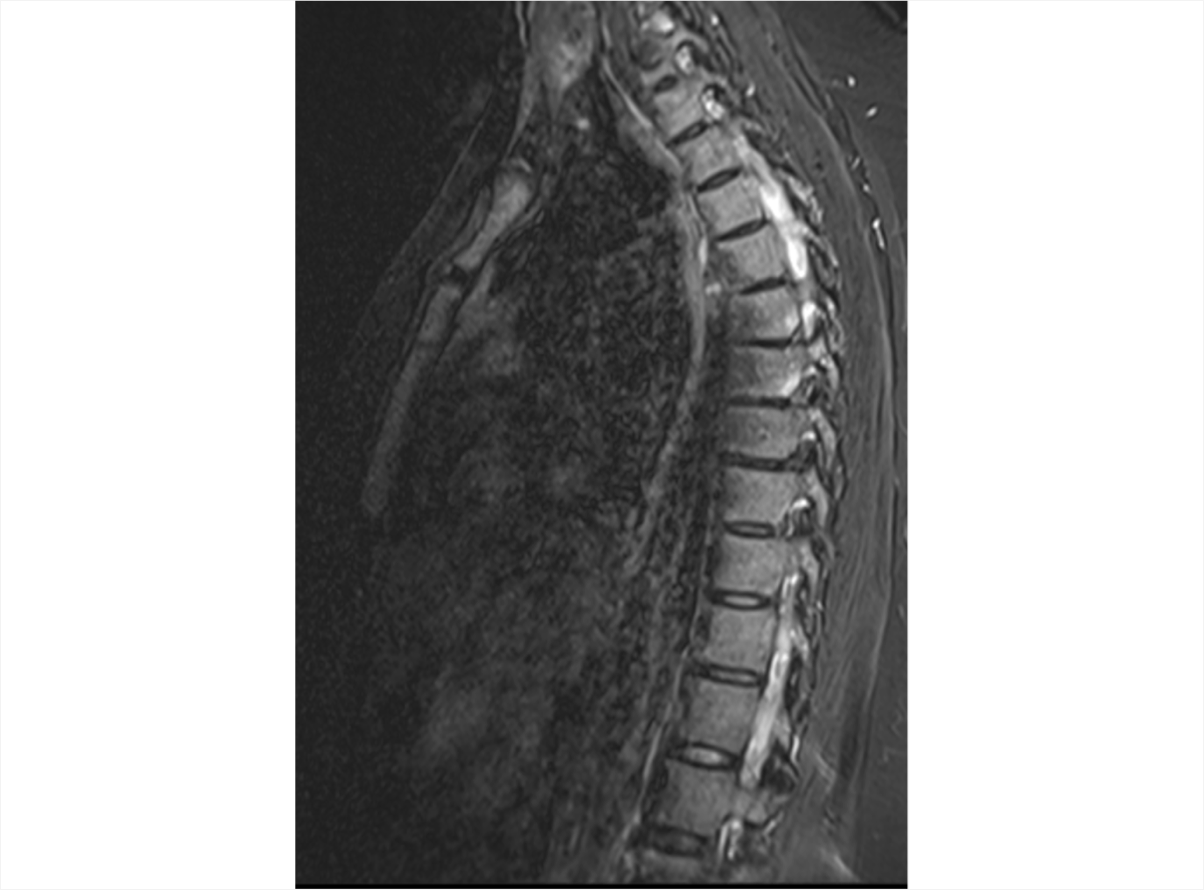
Axial Spondyloarthritis (AS,nr-axSpA) 3D Explorer
nr-axSpA
References
- Van Mechelen M, Gulino GR, de Valm K, Lories R. Bone disease in axial spondyloarthritis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;102(5):547-558.
- Maksymowych WP, Inman RD, Salonen D, et al. Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada magnetic resonance imaging index for assessment of sacroiliac joint inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;53(5):703-709.
- Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Baraliakos X, et al. The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) handbook: a guide to assess spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(Suppl 2):ii1-ii44.
- Østergaard M, Lambert RGW. Imaging in ankylosing spondylitis. Ther Adv Musculoskel Dis. 2012;4(4):301-311.
- Jurik, A. Spondylarthropathy Imaging. www.spa-imaging.org. Accessed July 26, 2023.
- Neerinckx B, Lories RJ. Structural disease progression in axial spondyloarthritis: still a cause for concern? Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19:14.
- Maksymowych WP, Inman RD, Salonen D, et al. Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada magnetic resonance imaging index for assessment of spinal inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;53(4):502-509
- Raychaudhuri SK, Saxena A, Raychaudhuri SP. Role of IL-17 in the pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis and axial spondyloarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2015;34(6):1019-1023.
- Watad A, Bridgewood C, Russell T, et al. The early phases of ankylosing spondylitis: emerging insights from clinical and basic science. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2668.
- Pialat JB, Di Marco L, Feydy A, et al. Sacroiliac joints imaging in axial spondyloarthritis. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2016;97(7-8):697-708.
- Braun J, van der Heijde D, Dougados M, et al. Staging of patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a preliminary proposal. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61(Suppl III):iii19-iii23.
- Poddubnyy D, Sieper J. Mechanism of new bone formation in axial spondyloarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(9):55.
- Osta B, Benedetti G, Miossec P. Classical and paradoxical effects of TNF-α on bone homeostasis. Front Immunol. 2014;5:48.
- Baraliakos X, Braun J. Non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis: what are the similarities and differences? RMD Open. 2015;1(Suppl 1):e000053.
- Kiltz U, Baraliakos X, Regel A, et al. Causes of pain in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017;35(Suppl 107):S102-107.
- Deodhar A, Reveille JD, van den Bosch F, et al. The concept of axial spondyloarthritis: joint statement of the spondyloarthritis research and treatment network and the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society in response to the US Food and Drug Administration's comments and concerns. Arthritis & Rheumatol. 2014;66(10):2649-2656.
- Bubová K, Forejtová Š, Zegzulková K, et al. Cross-sectional study of patients with axial spondyloarthritis fulfilling imaging arm of ASAS classification criteria: baseline clinical characteristics and subset differences in a single-centre cohort. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e024713.
- Ghosh N, Ruderman EM. Nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: clinical and therapeutic relevance. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):286.
- Deodhar A, van der Heijde D, Gensler LS, et al. Ixekizumab for patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (COAST-X): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395(10217):53-64.
- Rudwaleit M, Landewé R, van der Heijde D, et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part 1): classification of paper patients by expert opinion including uncertainty appraisal. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(6):770-776.
- Poddubnyy D, Rudwaleit M, Haibel H, et al. Rates and predictors of radiographic sacroiliitis progression over 2 years in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(8):1369-1374.
- Zhang S, Wang Y, Peng L, et al. Comparison of clinical features in HLA-B27 positive and negative patients with axial spondyloarthritis: results from a cohort of 4,131 patients. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:609562.
- Barhum, L. Verywell Health. www.verywellhealth.com/axial-spondyloarthritis-progression-6890574. Accessed July 26, 2023.
- Danve, A., Deodhar, A. Treatment of axial spondyloarthritis: an update. Nat Rev Rheumatol 18, 205–216 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-022-00761-z
- Schwartzman, S., Ruderman, EMR. A Road Map of the Axial Spondyloarthritis Continuum. Mayo Clin Proc. 2022;97(1):134-145
Abbreviations
AS: ankylosing spondylitis; ASAS: Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society; CRP: C-reactive protein; HCP: health care practitioner; HLA-B27: human leukocyte antigen B27; mNY: modified New York; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; nr-axSpA: nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis; NSAID: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug; r-axSpA: radiographic axial spondyloarthritis; SIJ: sacroiliac joint; SpA: spondyloarthritis; STIR: short tau inversion recovery
VV-MED-141368
Please rate your satisfaction with the content on the following statements:
Very Dissatisfied
Dissatisfied
Neutral
Satisfied
Very Satisfied