Comprehensive Obesity Care
Behavioral and Psychological Support
Patients experiencing weight bias may be hesitant to seek medical care. Consider a patient’s readiness for change and how to best collaborate with patients on their weight management journey.
How can you provide behavioral and socioemotional support in obesity management? Weight bias is present in healthcare settings and can negatively affect patients’ healthcare experiences, as well as their mental and physical health. However, patient-clinician collaboration can break the weight stigma/weight gain cycle. Behavioral interventions can help form collaborative relationships with patients, and the 5 As can provide a framework for weight management. These and other tools can help clinicians to incorporate multicomponent interventions into care plans. To learn more about how you can support the socioemotional needs of y our patients, view our Meet the Obesity Experts webinar series.
Internalized weight bias and weight stigma have a negative impact on both physical and mental health1,2
- Weight bias is negative weight-related attitudes, beliefs, assumptions, and judgments toward individuals with low or high weight1
- Weight stigma is the social devaluation of people because of their body weight, which leads to negative weight-based stereotypes and/or discrimination2
- Clinicians may characterize people with obesity as noncompliant and spend less time on consultations with them vs with their healthy-weight counterparts3
62%
of women and 54% of men with overweight or obesity reported hearing an inappropriate comment from their clinician4

Patients who experienced internalized weight bias were less likely to…
- Feel that their clinician was listening carefully to them
- Feel respected by their clinician for what they had to say
- Attend regular check-ups
- Perceive that they were receiving high-quality care
And were more likely to…
- Feel judged by their clinician because of their weight
- Avoid visiting their clinician because of discomfort during physical examinations
- Perceived weight stigma by people with obesity during medical visits is associated with worsened provider–patient relationships and adherence, lower perceived clinician empathy, and intentions to avoid future medical appointments5
- People who feel judged about their weight by a clinician report lower-quality interactions with their clinician, less frequent clinician–patient interactions, and lower trust in their clinician and are more likely to switch clinicians because of perceived differential treatment due to their weight5
Assessing and Addressing Patient Readiness for Change
The Transtheoretical Model features 6 stages of change that outline a person’s willingness, readiness, and commitment6
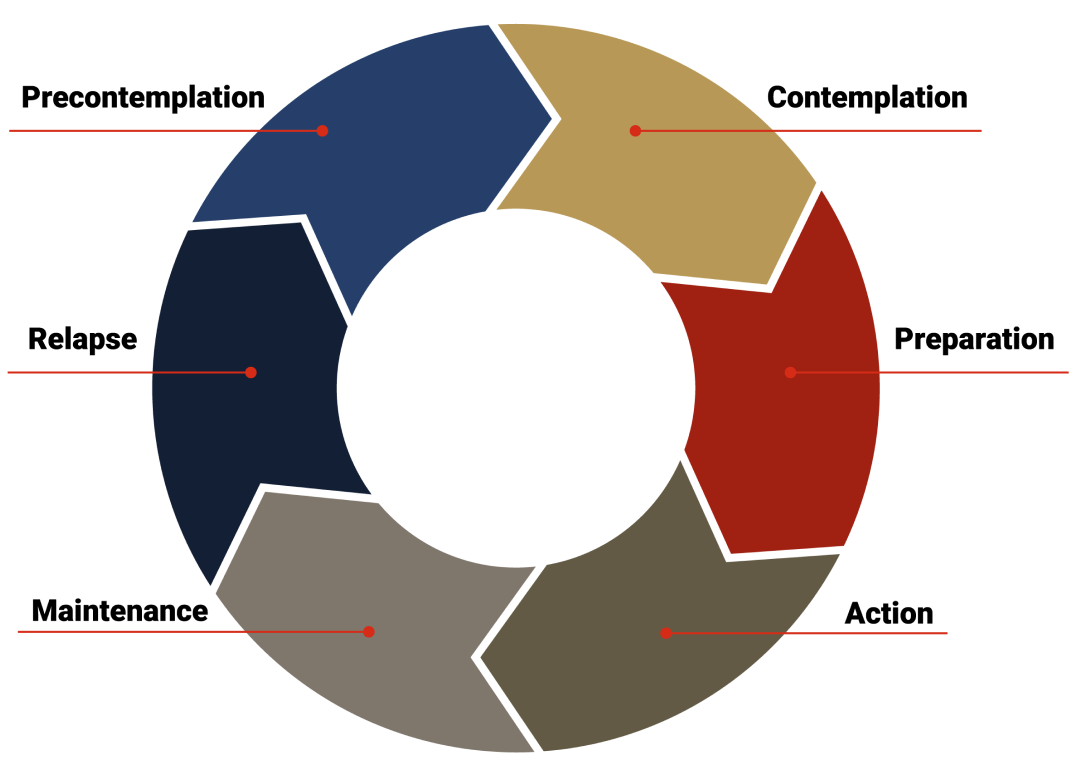
Weight loss interventions that utilize the transtheoretical model use multiple behaviors that exhibit greater compliance with body-weight control vs a single behavioral approach (eg, portion control, dietary fat, fruit and vegetable intake, and physical activity)7
Hesitating to change
Considering change
Intending to change
Implementing new habits
Sustaining habits
Reverting to old habits

Self-monitoring
positively influences self-awareness and personal behaviors by having patients intentionally survey and record their food intake and daily physical activities.9,10
Goals
|
Tools for planning and self-monitoring
|
|---|---|
| Healthier diet | Tools for planning and self-monitoring: Use an easy-recipe app for meals with a few fresh ingredients that cook quickly |
| More exercise | Tools for planning and self-monitoring: Record his walks with his dog in a fitness tracker |
| More positive mindset | Tools for planning and self-monitoring: See a therapist and begin journaling |
| Consistent commitment | Tools for planning and self-monitoring: Ask friends to join him for walks and meals |
References
- Alberga AS, Russell-Mayhew S, von Ranson KM, McLaren L. Weight bias: a call to action. J Eat Disord. 2016;4:34.
- Puhl RM, Himmelstein MS, Pearl RL. Weight stigma as a psychosocial contributor to obesity. Am Psychol. 2020;75(2):274-289.
- Phelan SM, Burgess DJ, Yeazel MW, Hellerstedt WL, Griffin JM, van Ryn M. Impact of weight bias and stigma on quality of care and outcomes for patients with obesity. Obes Rev. 2015;16(4):319-326.
- Puhl RM, Brownell KD. Confronting and coping with weight stigma: an investigation of overweight and obese adults. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2006;14(10):1802-1815.
- Puhl RM, Lessard LM, Himmelstein MS, Foster GD. The roles of experienced and internalized weight stigma in healthcare experiences: perspectives of adults engaged in weight management across six countries. PLoS One. 2021;16(6):e0251566.
- Prochaska JO, DiClemente CC, Norcross JC. In search of how people change. Applications to addictive behaviors. Am Psychol. 1992;47(9):1102-1114.
- de Freitas PP, de Menezes MC, Dos Santos LC, Pimenta AM, Ferreira AVM, Lopes ACS. The transtheoretical model is an effective weight management intervention: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):652
- Johnson SS, Cook B. Building motivation: How ready are you? In: Nigg CR. ACSM’s Behavioral Aspects of Physical Activity and Exercise. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams &Wilkins. 2014:103-128.
- Olateju IV, Ogwu D, Owolabi MO, et al. Role of behavioral interventions in the management of obesity. Cureus. 2021;13(9):e18080.
- Vallis TM, Macklin D, Russel-Mayjew S. Canadian adult obesity clinical practice guidelines: effective psychological and behavioural interventions in obesity management. Obesity Canada. Accessed November 27, 2023. https://obesitycanada.ca/guidelines/behavioural
- Lilly Patient Education Resources. Obesity. Accessed February 22, 2024. https://medical.lilly.com/us/diseases/patient-education-resources/obesity/obesity
- US Department of Agriculture. Dietary guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025. US Department of Agriculture; 2020. Accessed November 27, 2023. https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/sites/default/files/2021-03/Dietary_Guidelines_for_Americans-2020-2025.pdf
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Healthy weight, nutrition, and physical activity. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed November 27, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/tools/index.html
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Weight management. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Accessed November 27, 2023. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/weight-management
- Obesity Action Coalition. Education and Support: Treatment for Obesity. Obesity Action Coalition. Accessed February 22, 2024. https://www.obesityaction.org/education-support/treatment/
- The Obesity Society. Information for healthcare providers and patients. The Obesity Society. Accessed November 27, 2023. https://www.obesity.org/information-for-patients/
- Fitzpatrick SL, Wischenka D, Appelhans BM, et al. An evidence-based guide for obesity treatment in primary care. Am J Med. 2016;129(1):115.e1-e7.
VV-MED-156376
Please rate your satisfaction with the content on the following statements:
Very Dissatisfied
Dissatisfied
Neutral
Satisfied
Very Satisfied